If you are a webmaster, this is the stuff of nightmares:
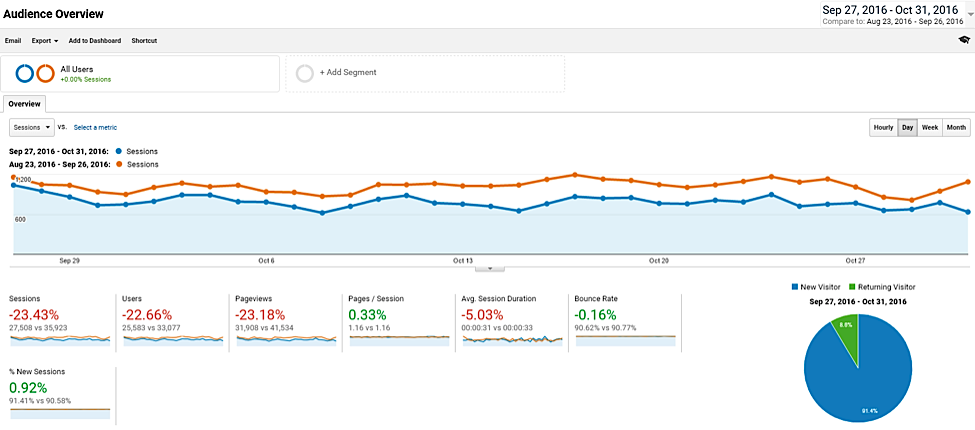
You check your analytics and see that there has been a significant decrease in traffic. In the above example, this company suffered a loss in traffic as a result of the Penguin 4.0 update.
However, not all traffic loses are as easily identified, especially now that Google is applying the Penguin in filter real-time. This means that webmasters do not have a specific date with which to associate specific updates.
There are different scenarios that can lead to a loss of traffic:
- You might have redesigned your website to improve the user experience, but a quick analytics examination revealed a steep drop in traffic shortly after you launched your new-and-improved site.
- Perhaps you saw a decrease in traffic after you moved your site to a new domain.
- Or maybe the decrease was gradual, resulting in an ongoing month-over-month decrease that significantly lowered your traffic and thus sales.
If these or similar scenarios sounds familiar, you’ve probably got two questions: What went wrong and how do you fix it?
A drop in traffic could be attributed to any number of problems. Most of those problems, however, fall into four broad categories:
- on-page issues
- off-page issues
- issues with user experience
- other miscellaneous issues
22 Reasons Why Your Organic Traffic Recently Dropped
Here are 22 of the most common reasons why your traffic might have decreased and, most importantly, how to fix the problem.
On-Page Issues
1) Panda Penalty
As of 2016, Panda is part of Google’s core ranking algorithm. The search giant’s most powerful anti-spam weapon is no longer just a recurring update. Most remedies to Panda involve improving content. Duplicate content, content that is designed for bots instead of readers, and low-quality content are all Panda magnets.
Try this fix: Perform a Panda Audit to identify any potential Panda issues and take the actions suggested.
2) Too Many 404s
Whenever possible, you should maintain the same structure on healthy URLs because changing URLs that have been performing well can be disastrous. Without a migration checklist and the right redirects, Google will reset the value of the old pages to the dreaded 404 error message, resulting in a massive drop out in your rankings.
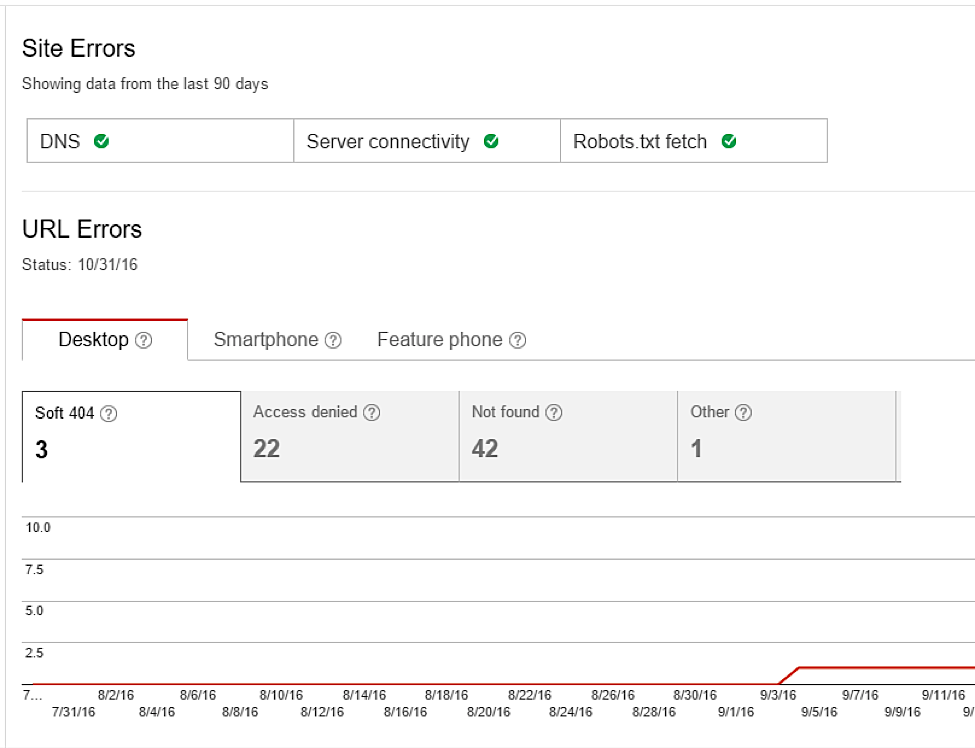
Try this fix: Use Google Search Console to identify 404s, and either fix them or use GSC to remove those 404s from their index.
 3) Incorrect Redirects
3) Incorrect Redirects
Correctly redirecting old pages so they point to their new URLs is critical. Failure to redirect them spells certain doom for your traffic. Permanent 301 redirects are almost always the best solution. Google does not like temporary 302 or 307 redirects nearly as much — and certainly not slow meta refreshes.
Try this fix: Check your site with the Link Redirect Trace extension to identify any faulty redirects or redirect loops that might be causing problems.
4) Problems with Website Migration (No Redirects)
The only thing worse for traffic than incorrect redirects is the failure to redirect at all. When no redirect is ordered, the page becomes a 404 error page — and too many 404s WILL cause a decrease in traffic from Google. It’s terrible for user experience and the last thing that Google wants is for their users to experience friction.
Try this fix: Use Screaming Frog to identify 404s and broken links, and then add redirects where necessary. When it comes to actual 404s, get them removed from Google’s index.
 5) Duplicate Content
5) Duplicate Content
Google has given conflicting advice about duplicate content, but one thing is certain — you should not make multiple copies of a page under different URLs. Many sites do this to create text-only, printer-friendly versions of pages. If, during your site migration, multiple versions of a page were created and you didn’t implement canonical tags, this would have caused issues with the Panda filter.
Try this fix: Run a duplicate content check using Copyscape and URL Profiler to avoid duplicate content. Then, either rewrite the duplicate content or remove it from the Google index using the no index, no follow meta tag.
Dive Deeper: Beginner’s Guide to Properly Using Rel Tags To Improve Your Site’s Rankings
6) Change in Site Architecture
When a website changes its internal organization, or architecture, some pages can emerge with fewer internal links, or end up linked to lower-value pages. Leaving orphan pages or removing link power to internal URLs could cause them to lose authority and drop in the rankings.
Try this fix: Crawl your site with Deep Crawl to identify orphan pages. Once you find them, add links to those orphan pages from other pages on your site and, if you can, build external links to those pages as well.
7) Change in Content Relevance
Content that no longer satisfies the search queries that directed visitors to your site in the first place can lead to traffic reductions. Irrelevant content could be old, outdated or not in line with what your audience wants. A tweak in the algorithm for your keyword category could impact your traffic drastically.
Try this fix: Identify which pages lost traffic by using Google Analytics and then add content to those pages, making sure they are relevant to the keywords they were previously ranking for. You can also do this using Google Search Console.
8) Deleted Pages
Deleting pages creates gaps in content. Sometimes webmasters try to improve the user’s journey by removing pages, but this alters the internal structure and removes previously earned rankings. Sometimes changing product names on your shopping cart or re-categorizing products could cause delete pages, which then create the dreaded 404s that we discussed in #2 above.
Try this fix: As with points #2 and #4, identify 404s and redirect or remove them from the Google index.
9) Site Speed
Improving site speed is one of the simplest and most effective ways to quickly improve traffic — and conversions. When Google experimented with increasing per-page search results from 10 to 30, the new format increased load time by just half a second. The result? A 20% drop in traffic. Nearly 50% of users will drop a website that doesn’t load in three seconds or less.
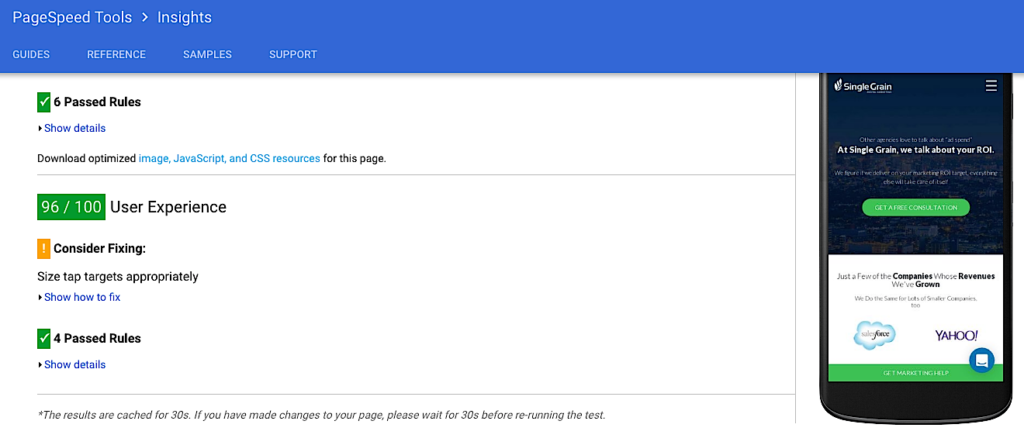
Try this fix: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insight tools to analyze and optimize. It’s as simple as typing in your website’s URL, like this example from Single Grain:
 10) Mobile/Responsive Traffic
10) Mobile/Responsive Traffic
By the end of the year, 58% of Internet traffic will be mobile. If you haven’t implemented responsive web design, which makes your website look great and load fast on any device, you’re going to experience larger and larger drops in traffic. Both your visitors and Google prefer this format, so if you haven’t already made your website mobile, do it now to see if you can get your traffic back up.
Try this fix: Use Google AMP to improve your mobile pages and make sure your site is responsive.

Dive Deeper: Top 10 Mobile Optimization Best Practices For E-commerce Sites
11) Specific Pages Not Relevant Anymore
If a page is no longer relevant, use a 301 redirect to point it to a page that is. For example, if your website no longer sells red v-neck T-shirts, point your old red v-neck T-shirt page to the main T-shirt page. Do not, however, redirect an old page to your site’s home page. You want to stay as categorical as possible and maintain relevancy, otherwise you are negatively impacting the user experience which will have negative results.
Try this fix: Perform a content audit to determine which pages are no longer relevant. Use a tool like URL Profiler to help crawl and categorize your pages, and then determine their relevancy.
12) High Ads-to-Content Percentage
In 2014, Google began targeting pages that have an unhealthy ads-to-content ratio above the fold. You know those sites: way too many pop-up or other types of ads that take up so much space you can barely access the content. If you can trace the drop in your traffic back to February, 2014, that’s probably the culprit.
Try this fix: If you have large or multiple ads above the fold, try placing some or all of them below the fold or reducing the number and size of ads above the fold.
Off-Page Issues
13) Algorithmic Penguin Penalty
Penguin penalties can result in a fast, steep drop in site traffic, but before you try to fix them, you have to find out if Penguin is actually the source of your problem. The Fruition Google Penalty Checker makes it easy. If you determine that Penguin is the problem, fixing it is a multi-step process that requires more explanation than is possible here.
Try this fix: Follow this guide to identify whether or not you have a Penguin penalty and how to have it removed.
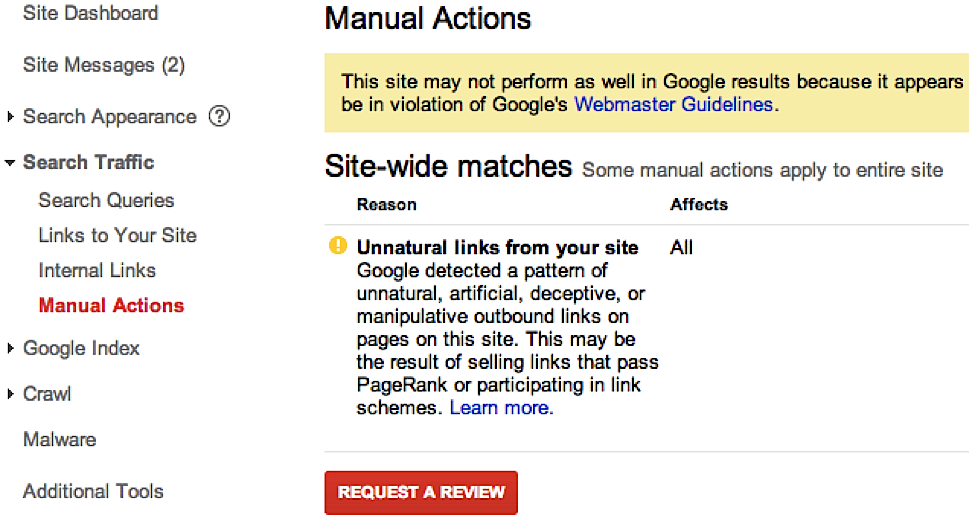
14) Manual Action Penalty
Unlike algorithmic penalties such as Penguin, Panda or Hummingbird, manual action penalties are exactly what they sound like. Google may have manually penalized your site for what it perceived as spam or other shady behavior, including unnatural links, a suspect structured markup, cloaking, suspicious redirects and weak content.
Try this fix: Check Google Search Console to see if you have a manual action penalty. If you do, you will then need to follow the same steps as you would with a Penguin penalty, but you will also need to send a reconsideration request. Here is a great guide from Moz to manual penalties.
15) Not Enough Domain Authority
If you have less domain authority than your competitors, you will almost certainly not be able to make up for lost ground with strong content and page optimization. Also called link juice or domain trust, domain authority is an umbrella term for any off-site elements that could impact your site.
Try this fix: Try using influencer and blogger outreach to earn quality links for your content.
Dive Deeper: Starting From the Bottom: How to Build Up Your Domain Authority from Scratch
16) Not Enough Page Authority
Page authority is an assigned metric, measured on a 100-point scale, designed to reveal how well a page will perform in Google search rankings. The page needs to not just be relevant, but also to have enough link juice to rank it above other relevant pages.
Try this fix: Download the backlinks of top pages ranking in the SERPs for your keywords, and try to get the same backlinks for your own pages. For example, if your keyword is “blue widgets,” identify the sites that are ranking for blue widgets, download their backlinks using a tool like Ahrefs, and contact the same sites to earn links to your “blue widgets” page.
User Experience Issues
17) Low Time on Site
This is arguably one of the most important metrics regarding traffic and average session duration, and reveals how much — or how little — time users are spending on your site. The average across all industries is between two and three minutes. You want your users to stay on your site as long as possible, showing Google that the visitors they sent you found what they were looking for.
Try this fix: Use Google Analytics to identify which pages have low time on site and then update or upgrade the content on them.
18) Low Pages Seen Per Visit
Pages seen per visit indicates how much content visitors are actually consuming once they land on your site. When numbers are high, it usually indicates that the first piece of content a visitor encountered was strong enough to entice them to check out a second, third or fourth piece of content. You’ll want to increase this metric to show stronger user engagement signals to Google.
Try this fix: Add a “related pages” widget to your site so that you show similar articles to your visitors in order to increase the amount of pages they visit, like this Single Grain example:

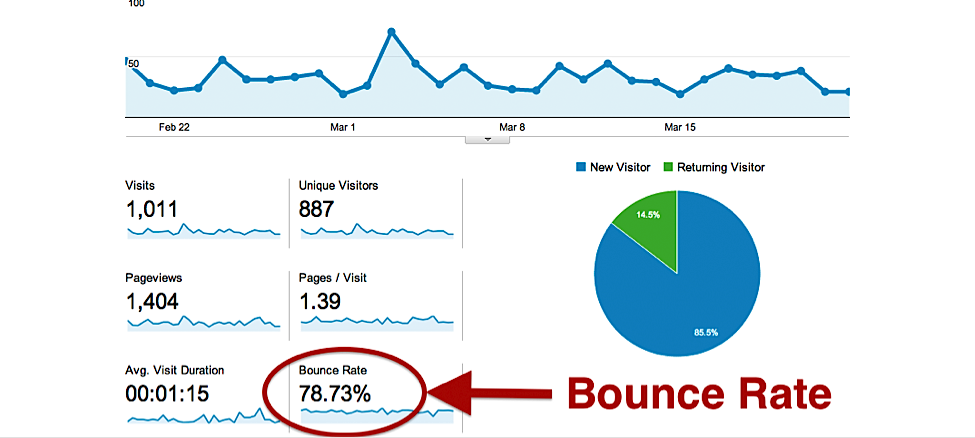
19) High Bounce Rate
High bounce rates generally indicate unhappy users fleeing your site soon after they arrive. High bounce rates can spur Google into lowering your rankings, which can, in turn, further reduce your traffic.
Try this fix: Add high-quality content that is of value to your visitors to your pages to make them more in-depth or relevant. Use Google Search Console to see which keywords that a page ranks for, and add additional content related to the specific keywords that people are searching for.
Dive Deeper: B2B SEO: How to Rank Your Business Website Higher in Search
20) High Pogo-Sticking Rate
When visitors have trouble finding the content they’re looking for on your site, they are forced to waste both clicks and time bouncing between different pages on a site. Since this can be caused by misleading or irrelevant information, Google doesn’t like it — and neither do your visitors. Google can measure this by the amount of time visitors spend on your site after they’ve left the SERPs.
If they immediately come back, it’s obvious they didn’t find what they were looking for. If they stay for a long time and then come back, perhaps they reviewed the content but needed additional information. If they stayed for a long time and don’t come back, it’s likely that they found what they were looking for.
Try this fix: Check Google Search Console for your click-through rate of specific pages, and optimize those pages to improve CTR and user engagement signals.
Miscellaneous Issues
21) Competition Is Rising
Even if you did nothing wrong, a new competitor may have siphoned off some of your visitors. You need to keep an eye on the competition to make sure that you are keeping up and that your KPIs continue to be just as strong.
Try this fix: Perform competitive analysis twice a year, tracking metrics such as organic keywords and visitors from SEMrush, as well as referring domains in order to keep up with what your competitors are doing.
22) Seasonal Fluctuations
Some businesses are inherently seasonal, a trend that is reflected in their traffic patterns. If a website sells beach chairs, for example, it is highly likely that traffic will drop in the winter.
Try this fix: Use Google Analytics to search for seasonal fluctuations in the past, and make sure you are aware of these trends. Think about what you can do to increase site visitors during the off-season.
Most reasons for sudden drops in traffic can be traced to on-page issues, off-page issues, problems with user experience and a handful of other potential causes that don’t fit neatly into any one category.
The good news is, there is almost always a remedy — but you have to first identify the problem. Follow the suggestions in this post to figure out where the problem is, and you’ll be well on your way to a speedy recovery!



