If you’re wondering how good your website’s SEO is, you’re in the right place.
This article is a beginner-friendly guide to SEO scoring; you’ll learn what SEO scoring is, which specific areas can be scored, and how to do it.
We’ll explore some different approaches, metrics, and tools that you can use to grade different aspects of your SEO, and find out where you can improve.
We’ll look at:
- What is an SEO score?
- What’s the difference between SEO score and Domain Authority?
- 5 easy methods to score your website’s SEO
Ready? Let’s get started!
What Is an SEO Score?
An SEO score refers to any third-party metrics (provided as a final result, or “score”) that measure how SEO friendly your website is.
You can use tools to score various aspects of your SEO efforts which will show you:
- How well optimized your written content is
- Your technical SEO site health
- Whether your content is fresh and up to date
- Your website’s mobile friendliness
- Your website’s load speed and user experience
- How many backlinks a site or page has
Most of these scores are not directly calculated by Google. They’re created by third parties, with the aim of helping SEO practitioners (especially beginners) measure and analyze specific areas of their work.
It’s important to remember the limitations of these tools (which we’ll address case-by-case below), but they can be a very helpful starting point as you embark on your SEO journey.
Dive Deeper:
* 10 Effective SEO Techniques to Drive Organic Traffic in 2023
* 6 SEO Trends You Can’t Ignore in 2023
* 9 Quick SEO Tactics That Only Take 10 Minutes to Implement
Difference Between SEO Score and Domain Authority Score
Some SEO platforms like Moz, Ahrefs and Semrush use a metric like ‘Domain Authority’ or ‘Domain Rating’ to reflect the overall strength of a domain.
This is calculated based on the backlinks pointing towards that site, and is a general indication of how well the site should rank in search engine results pages:
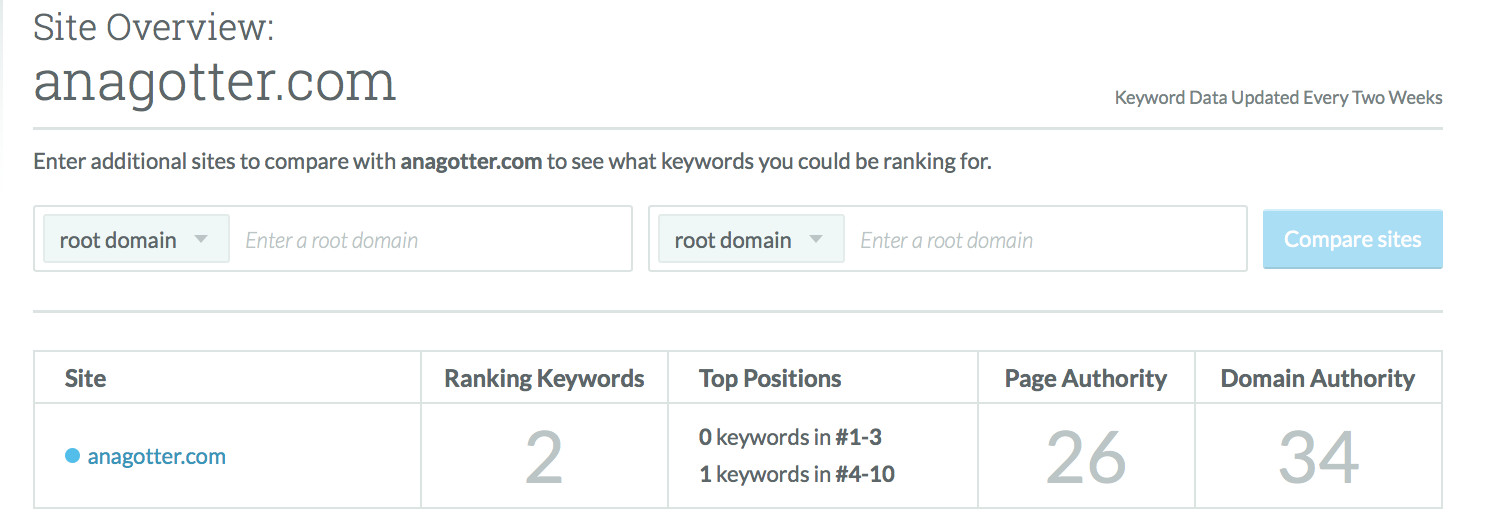
The above image is from a small business that earns a healthy 34 Domain Authority rating, while the image below is from a large business that earns an impressive 89 Domain Rating.
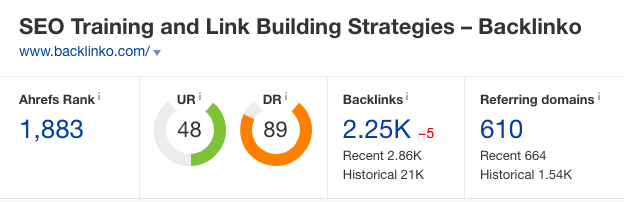
They’re not directly used by Google, but these third-party metrics are widely accepted in the SEO community as a useful measure of a domain’s strength.
You could consider domain authority to be one type of SEO score, but it is not the only type. This metric is limited to scoring your domain’s backlink profile (i.e. how many other sites are linking to your content). It fails to consider other ranking factors like technical SEO, content optimization (and relevance), user experience, and more.
Dive Deeper: Domain Authority: How to Increase Your Ranking Score from Scratch
How to Score Your Website’s SEO: 5 Easy Methods
Now that you know what the heck an SEO score is and what it’s used for, you’ll want to find a good SEO score checker. As mentioned, there is no one tool for this purpose. Instead, we present you with a list of five of the best tools and methods to quickly score your site’s SEO in different capacities.
The first area in which you can score your website’s SEO is your written content by using content optimization.
Content optimization refers to the process of ensuring that you hit the right:
- Primary and secondary keywords
- Approximate word count
- Key subtopics
- Questions
- Level of readability
- Search intent
- And more
If you get some of these elements wrong, your content simply will not rank – and all the resources spent on producing it won’t return an ROI.
For example, if a search term demands an in-depth 4,000-word answer and all the current ranking pages are this detailed, and you try to rank with a 500-word summary, it just won’t work. This is described by Matt Diggity as the ‘black sheep effect’.
And the reverse is also true. You don’t want to stand out for being the only web page that is trying to rank a 10,000-word essay for a search term which should be concisely satisfied with a 1,000-word landing page.
Here’s an easy step-by-step process you can follow to score your content.
Once you’re in, head to the Content Editor feature, and hit ‘+New Article’.
Enter Your Primary Keyword
This step is the same regardless of whether you’d like to score existing content or start new content.
It’s normal for this to take a couple of minutes to process.
Import Your Content (or Start Writing!)
Next up, you’ll see a screen that looks like this:
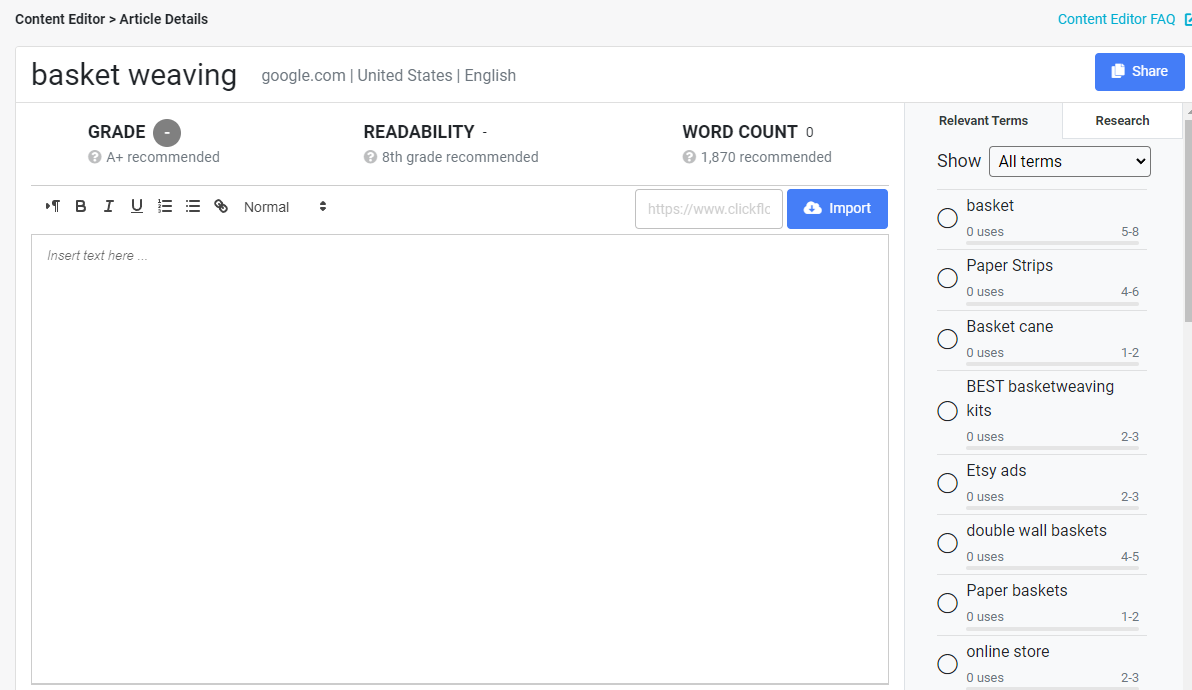
Straight away, you’ll see some of the elements that Content Editor can score your content on:
- Overall grade (where A+ is the best)
- Readability recommendation (how important it is to use simple or technical language)
- Recommended (and current) word count
- Primary and secondary keywords (and their recommended densities)
If you want to get a grade for content you’ve already published, you can drop in your URL and hit the ‘Import’ button to pull in the text:
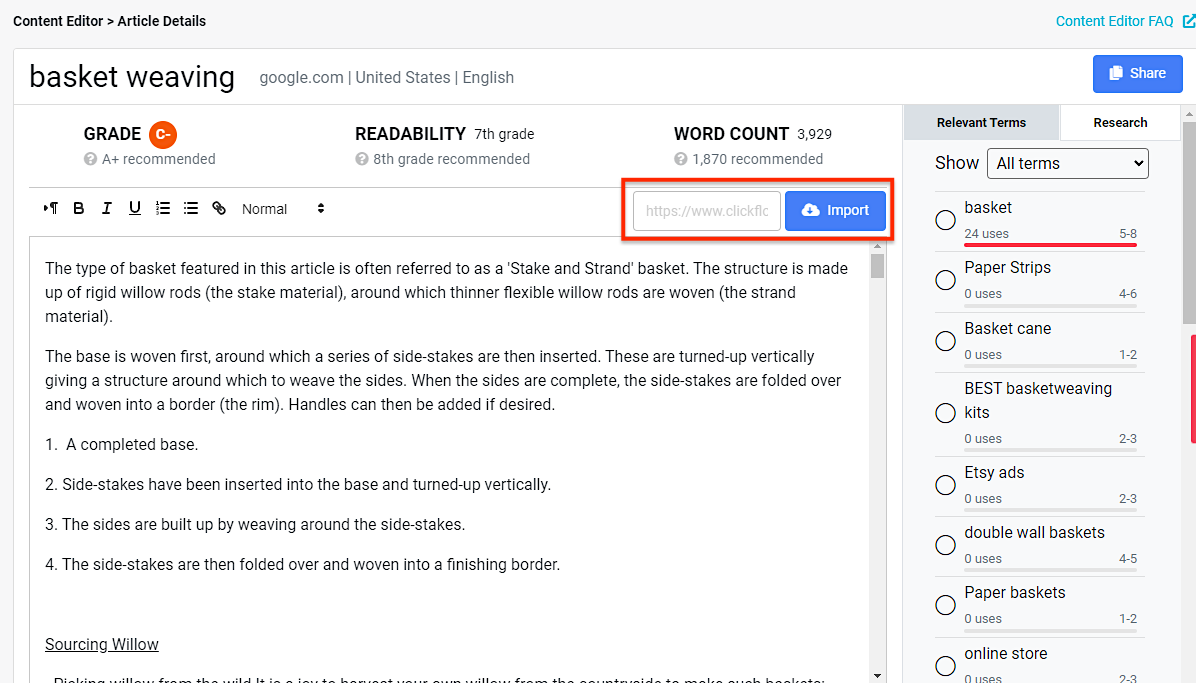
Now you’ll have a grade for your content, together with easy-to-understand recommendations on how to improve it. Add and remove content, paying attention to the relevant keyword terms listed on the right-hand side, and watch your content score increase.
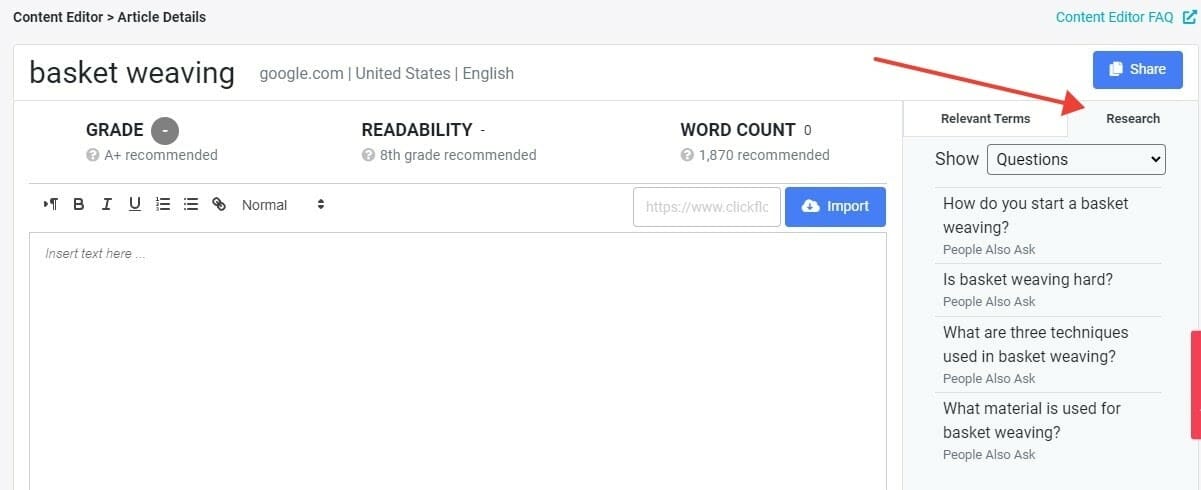
Pro Tip: Click on the ‘Research’ tab to find a list of People Also Ask questions pulled right from Google to include as FAQs or subtopics. If you answering these commonly asked questions, this will enrich your content with better searcher intent:
Limitations of Content Optimization Scoring
The one caveat to this technique for scoring content is that it requires some level of competition. If you find a truly unique opportunity where there isn’t any good content out there right now, the recommendations generated by a content optimization tool won’t be useful. You’ll need to innovate!
For the vast majority of search terms, though, you’ll have no trouble – there’s a lot of content out there (and 4.4 million+ added per day!).
Lastly, you should also remember that even a perfect content optimization score doesn’t guarantee a number one ranking in the SERPs. There are other factors at play, including internal and external backlinks, topical authority, and more.
Method #2: Score Technical SEO Health with Ahrefs’ Site Audit Tool
Technical SEO is another area in which you can score your website. Technical SEO can refer to aspects like:
- Ensuring that your web pages are crawlable and indexable
- Managing duplicate content with canonical tags
- Load speed and security factors (e.g. using https)
- Response codes (301 redirects, 404 errors, etc.)
- Other factors like hreflang, javascript, URL structures, and more
If you’re not familiar with them, some of these issues can feel daunting to tackle. Luckily for us, there are many tools out there which help to navigate technical SEO. They can give your website a general site health score, flag the SEO errors that are holding back your site, and explain how to improve them.
Ahrefs’ Site Audit is one such tool (but there are several other alternatives that do the job, too). Here’s a guide to using Ahrefs to score your website’s technical SEO health.
Head to the Site Audit Tool and Create a New Project
If you don’t have an Ahrefs account already, you’ll need to create one first. They have a 7-day trial for $7 which you can use for this purpose.
Once you’re in the dashboard, you’ll see an option for ‘Site Audit’ in the top navigation bar.
Head there, and click ‘+ New Project’.
You’ll get two options: Google Search Console import or add it manually:
Connect your Search Console account, and add your website as a project.
Wait for Ahrefs to Crawl Your Website
After you’ve added your project, when refreshing the Site Audit page you’ll see something like this:
Ahrefs will automatically start to crawl your site, which can take a while (the bigger your site, the longer it will take). Allow 15-30 minutes as a minimum, even for smaller sites.
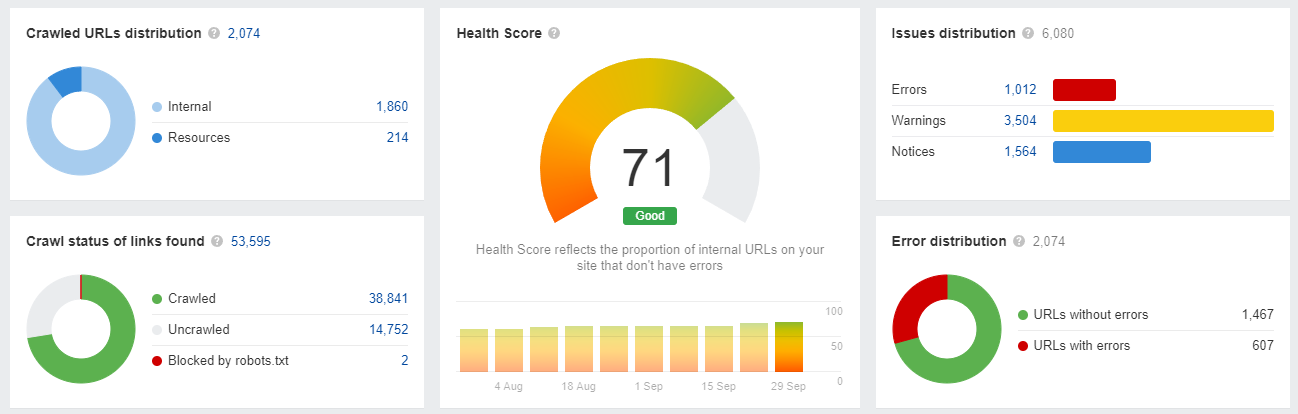
Once the crawl is complete, you’ll get an overview of your site’s technical SEO, including an overall Health Score:
View ‘All Issues’ to See What’s Holding Your Site Back
Using the left sidebar menu, look for ‘All Issues’.
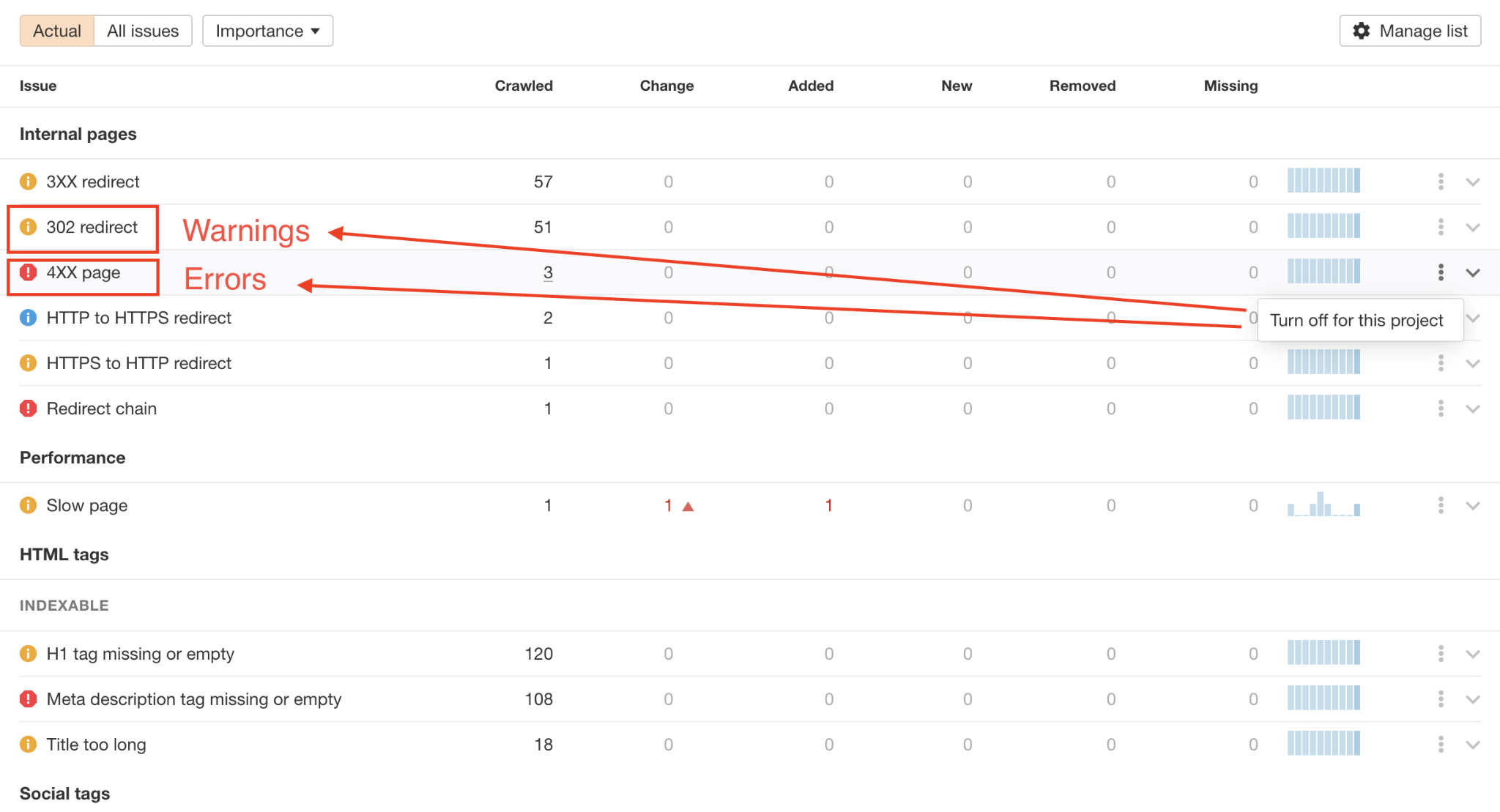
On this page, you’ll see all the different elements that could be improved on your site. They’ll be categorized in groups. Issues could be related to:
- Internal pages
- Indexability
- Links
- Redirects
- Content
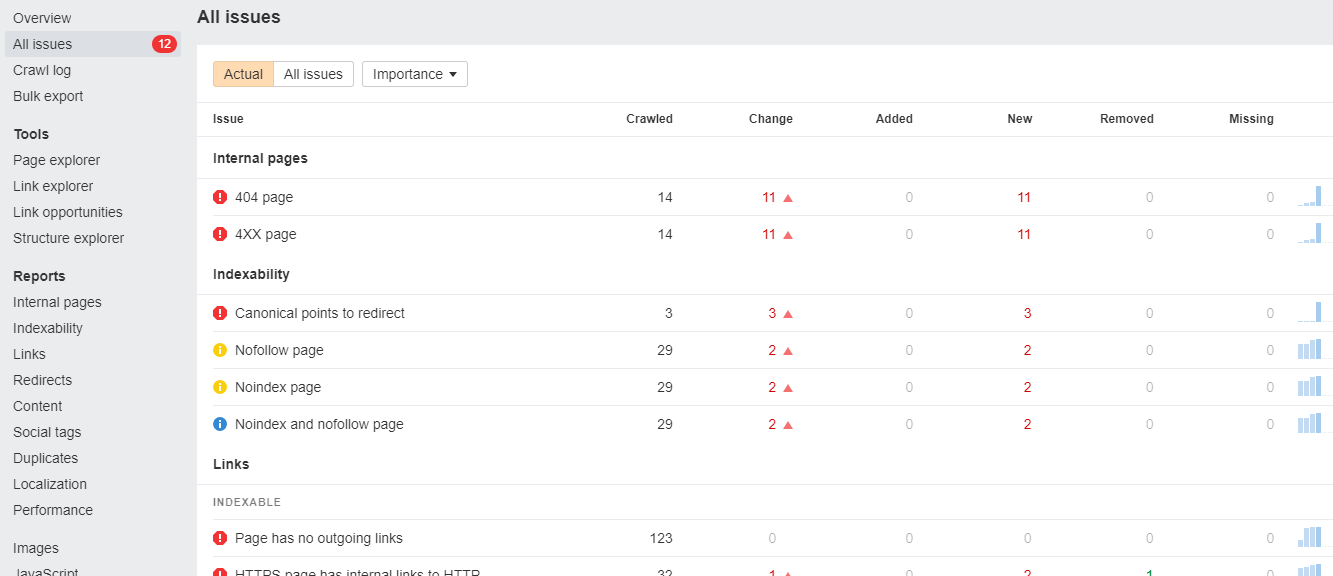
Issues are also assigned a level of importance – Errors, Warnings, and Notices – to help you prioritize.
Learn More about Specific Issues
Now you can go through each of the highlighted issues. Clicking on one will open up a helpful explanation tab with more information, how to fix the issue, and a link to find the affected URL.
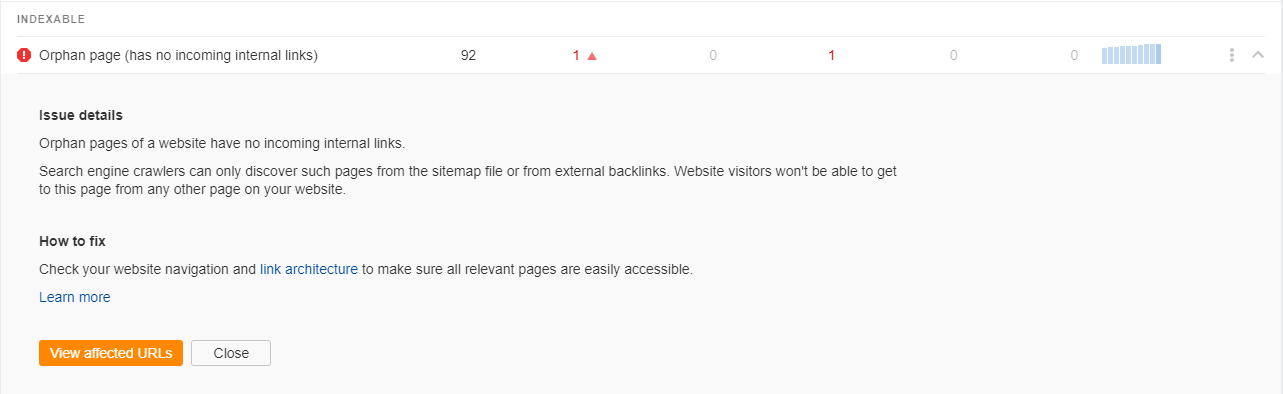
Limitations of a Site Audit Scoring Tool
Site audit tools, including Ahrefs’ Site Audit, flag things that don’t always need fixing.
For example, you might find notices for things like ‘page has outgoing nofollow links’ or ‘page has a low word count’. These could very well both be intentional, with no need to fix it, and no benefit found by addressing them.
As you get more familiar with the tool, and technical SEO in general, you can choose to disregard issues (and prevent them from affecting your health score):
Method #3: Score Your Page Performance with Core Web Vitals
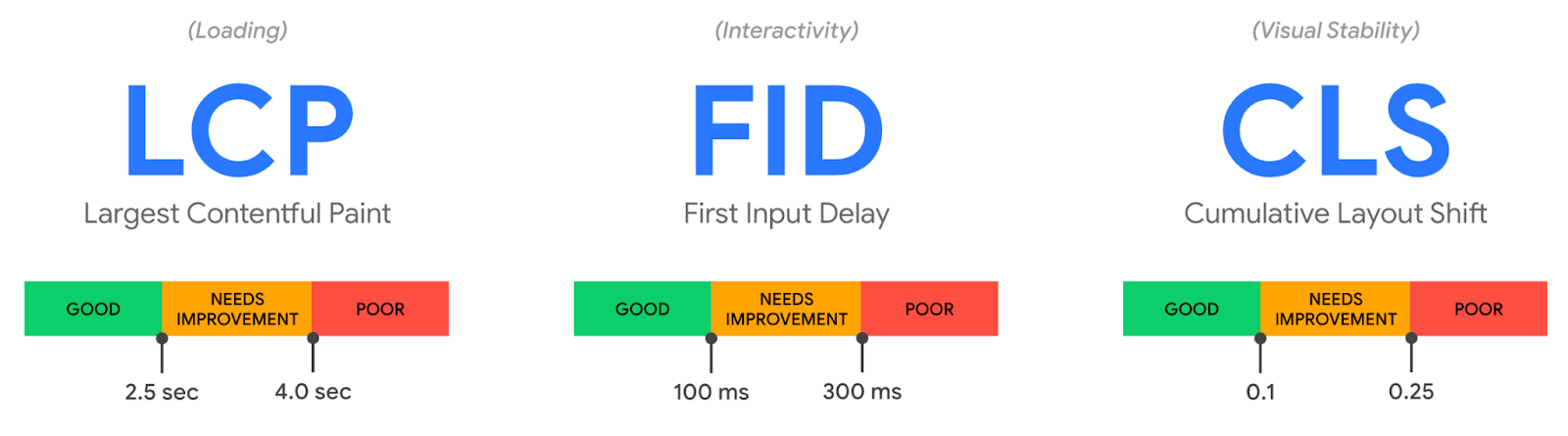
Core Web Vitals are a relatively new ranking factor (since 2020). CWV refers collectively to a number of page experience metrics, including:
- Largest contentful paint (LCP). This measures how long it takes for a real user to load and interact with your web page.
- Cumulative layout shift (CLS). CLS measures how visually stable your page is when loading.
- First input delay (FID). This measures how quickly a user can begin interacting with your page.
Google has guidelines on what counts as a ‘good’, ‘needs improvement’, or ‘poor’ grade for each of these:
You could argue that CWV is a part of technical SEO, which we’ve already discussed. That being said, it’s such a hot topic right now that it deserves some dedicated attention.
There are several free tools that you can use to get your website’s CWV scores.
Check CWV Scores in Google Search Console
The first thing you can do is check your CWV scores in Google Search Console. To do that, look under the ‘Experience’ subheading in the left sidebar, and click on ‘Core Web Vitals’:
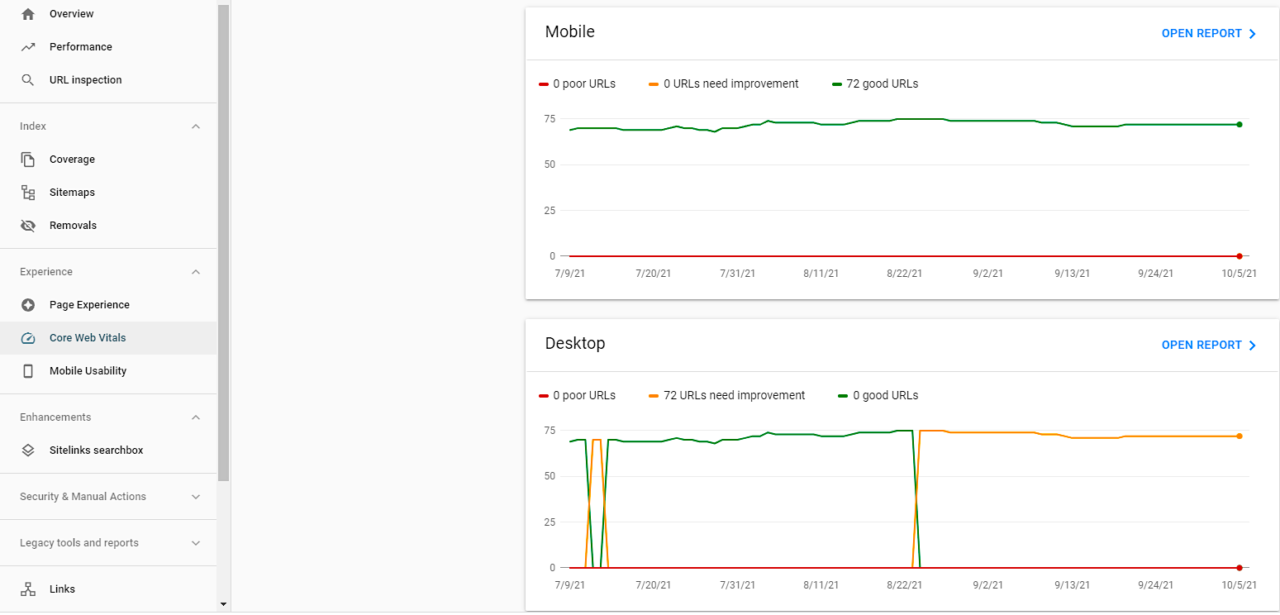
You’ll get a breakdown of your URLs, with each being graded as ‘poor’, ‘needs improvement’, or ‘good’. If you have any required improvements, Google will let you know which of the three CWV metrics it relates to:
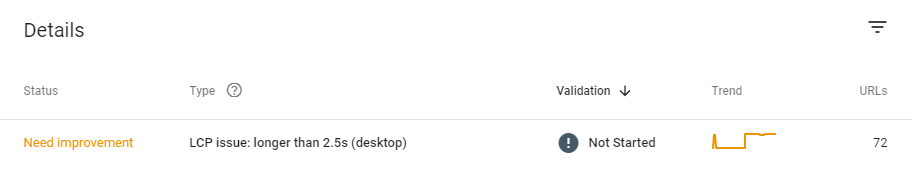
Dig Deeper in the PageSpeed Insights Report
To take it one step further, you can use Google’s PageSpeed Insights report to dig deeper. It uses the same data set that powers the Search Console report, but offers more helpful suggestions on how to actually improve performance.
Simply enter your URL, and wait a few seconds for the tool to analyze your site:
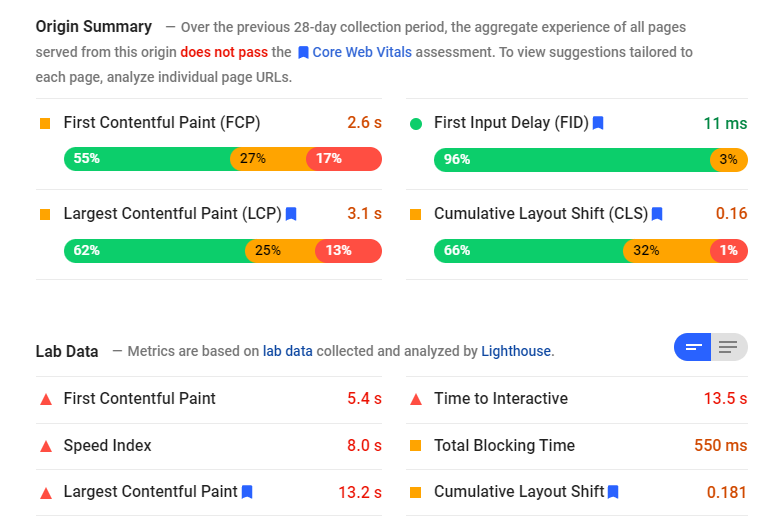
You’ll get a summary of your scores in each area, which will correlate with what you found in the Search Console, but with more precision:
As you scroll further down, you can use the filters to show only issues that are relevant to a specific metric, which is helpful to drill down and find areas to work on:
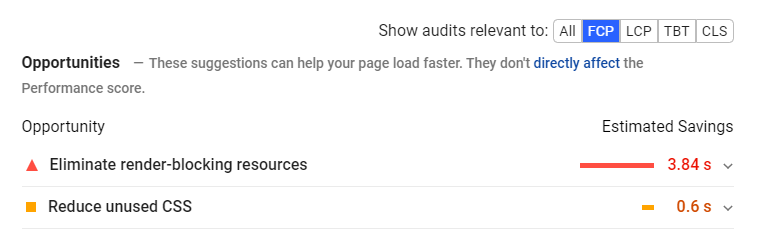
You might find that fixing just one or two big issues goes a long way with CWV scores.
Limitations of Using Core Web Vitals Score
A study by Sistrix found a small increase in visibility for sites with good CWV scores but, more notably, measurably less visibility for those who had poor scores.
Working on your CWV often won’t have an immediate significant uplift to your search traffic, and even if it does, it’s hard to measure (and attribute it to specifically that work). On the flipside, though, not working on it is more likely to hold back your performance.
Lastly, don’t obsess over getting perfect scores. There’s a point at which further page experience improvements become impossible, impractical, or cause detriments to other areas. For example, you’ll always need a cookie consent notice, which is likely to cause a (minor) CLS issue, but it’s still necessary. Don’t sweat it.
Dive Deeper:
* How to Prepare Your Site for the New Google Page Experience Update
* What Is the Google BERT Search Algorithm Update?
* CWV Update: Why Google Keeps Changing How It Measures Your Site’s UX (and What to Do About It)
Method #4: Measure Content Decay to See Where Your Traffic Is Declining
It’s an unfortunate fact of life for SEO and content marketers that, even once you achieve that glorious number one position, it might not stay there forever.
Search intent evolves, SERPs get new features, content gets outdated, competitors produce better content, and so on. There are a lot of ways for positions to slip. This is known as content decay, and as a website gets older and larger, it becomes more and more a necessary part of your strategy.
Although there isn’t a single metric or ‘score’ that you can give your entire site for content decay, you can look page-by-page and find out how much (if at all) they’ve dipped.
It’s possible to manually analyze your Google Analytics and/or Search Console data, but it’s quite a time-consuming process filled with spreadsheets and pain.
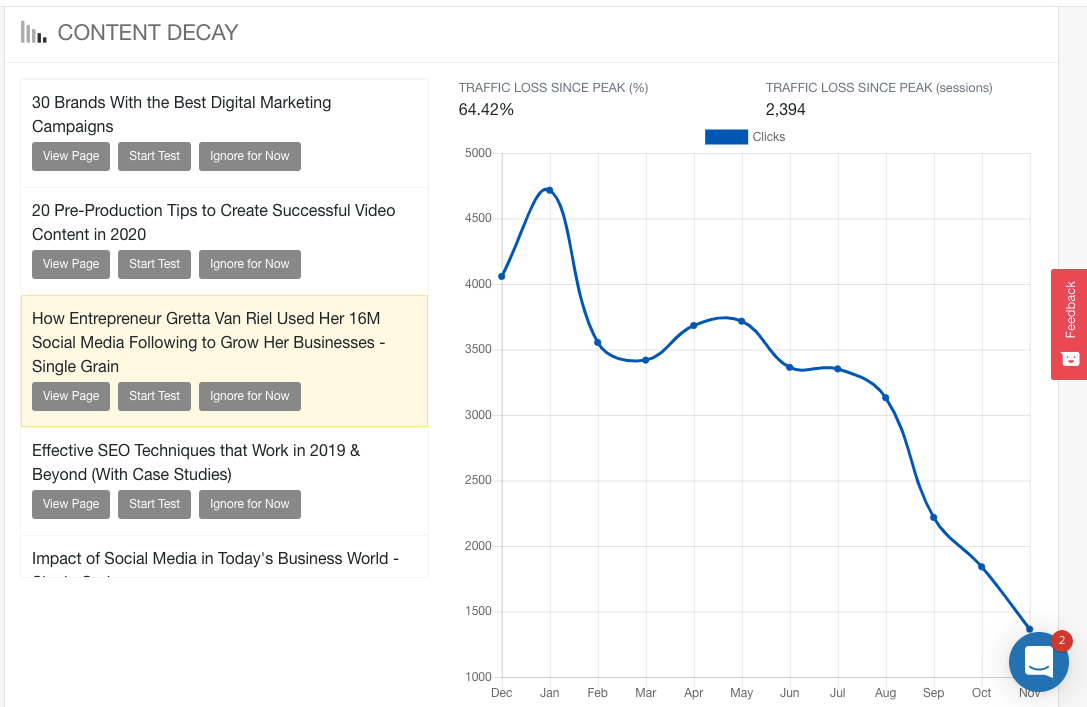
There, you’ll see the pages on your site that have seen a decline in traffic. By default, they’ll be ordered by which pages have lost the most traffic, with the biggest drop at the top:
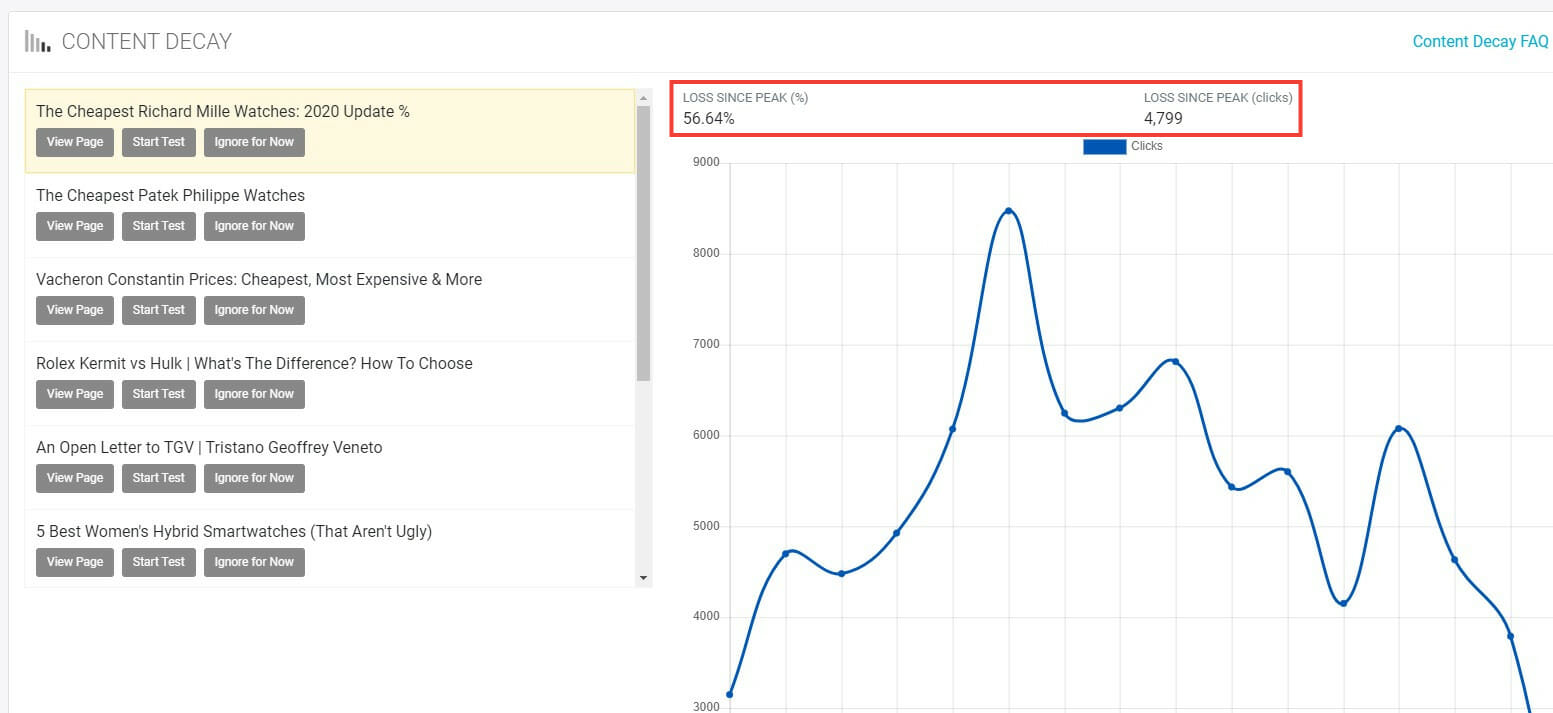
At a glance, you’ll be able to see the performance over time, what the peak traffic was, and how much traffic has dropped. You can use this information to prioritize your content resources and efforts.
Remember, Google prioritizes relevant, fresh content that is up to date with the latest information. An easy way to gain back your lost traffic from your content decaying pages is simply to update them. You can do this by:
- Expanding your old blog posts with new sections to make them more comprehensive
- Updating older posts with new information to make them relevant again
- Changing the keywords, particularly if you had optimized a post for trending keywords
- Getting more links (external and internal) to top content
Check out this 2-minute overview video to see how the Content Decay tool works:
Limitations of Using Content Decay
The only potential downside of monitoring and tackling content decay with a tool like this is opportunity cost. Updating content takes time, and with limited capacity, there are other things you could be doing.
Just because a post has declined in traffic, doesn’t necessarily mean it needs updating. Take a minute to ask the right questions:
- Is this post generating traffic that is relevant to my current goals?
- Does this post generate revenue? If not, does it at least push users down my funnel?
- Does this post generate brand awareness or backlinks?
Dive Deeper: What Is Content Decay and How It Affects Your SEO
Method #5: Measure Your Backlink Profile with Ahrefs Site Explorer
It’s no secret that backlinks are still one of the biggest ranking factors. For that reason, SEO professionals use metrics to help measure the strength of backlinks.
Different tools have different names for their backlink metrics, but they fundamentally work in a similar way. We’ll use Ahrefs again and look at their Site Explorer tool.
In Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, you’ll find two main metrics to score backlink strength:
- Domain rating which, as described earlier, measures the overall strength of a domain’s backlink profile, considering both the quality and quantity of its backlinks.
- URL rating which measures the strength of backlinks for a specific individual page. Internal backlinks are counted here, as well as external.
Both metrics work on a scale of 0 to 100, where higher is better.
In order to get your backlink profile score, there’s not much of a step-by-step process required here. All you need to do is sign up for an Ahrefs trial (or free account), and put your URL into the Site Explorer:
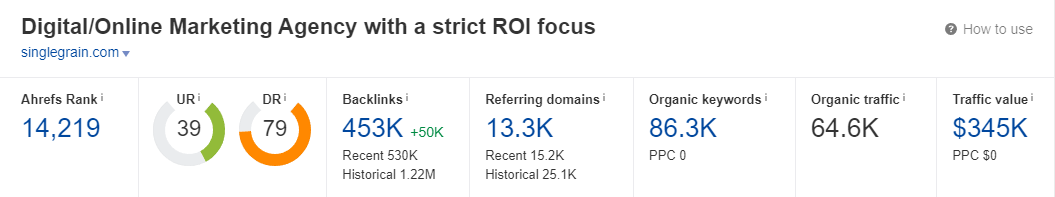
Straight away in your overview dashboard you’ll see:
- Number of backlinks pointing to your site
- Number of unique referring domains
- Domain rating
- URL rating (of the URL you entered, probably your homepage)
To dig into specific pages, you can then navigate to the ‘Best by Links’ report in the left sidebar. There, you’ll find a list of your top URLs based on URL rating (how many backlinks pointing to those specific pages):
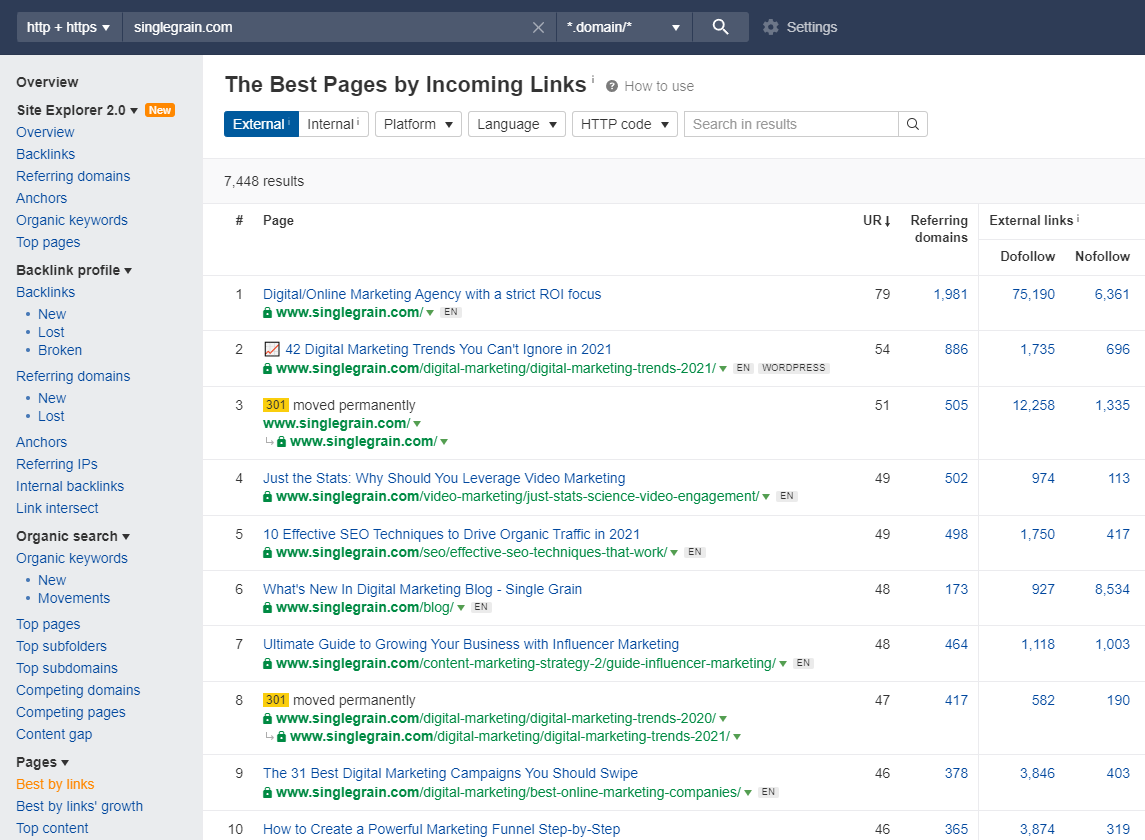
That’s it!
You can then use Site Explorer to monitor your DR score over time as you build backlinks:
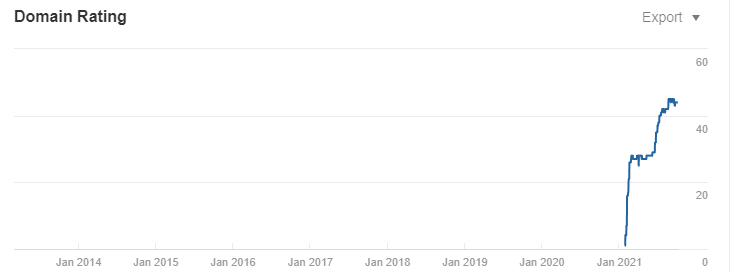
Since both DR and UR work on a logarithmic scale, you’ll see quick improvements in your scores early on as you build quality backlinks. It’s a lot easier to go from 0 to 10 than it is from 70 to 80, for example.
Limitations of Using a Backlink Scoring Tool
It’s important to remember that higher domain rating does not always equal more traffic and revenue. Since domain rating is based solely on backlinks, it’s actually possible for a site to have a high DR (e.g. 80+) with very little traffic, if any.
I don’t know about you, but I’d rather have a backlink from a DR20 site with 10K+ in relevant monthly traffic, than a DR80 site with no traffic!
Use this metric to monitor the efforts and effectiveness of your link building activities, but apply common sense, too. Sometimes a great backlink from a relevant page will help your rankings, without moving the needle (when the ‘needle’ is your DR score!).
Conclusion
An SEO score isn’t one single number that you can apply to your entire website. Rather, you’ll need to break it down into subsections in order to score your SEO performance.
Finding your website’s SEO scores can be quick and easy, and it doesn’t have to break the bank. But taking the time to do so will go a long way in helping you figure out where to focus next in your SEO efforts.
Good luck!
SEO Score FAQs
How do I check my SEO score?
To score your website’s SEO performance, you must break it down into different categories. For example, if you want to know how SEO-friendly your content writing is, you can use a tool like ClickFlow’s Content Editor. It will give you a grade, and recommended areas for improvement.
What should your SEO score be?
This question doesn’t have a straightforward answer. It depends on which type of score we’re talking about, and even then it still depends on your specific circumstances.
A higher score is always better, especially for something like a content optimization score or your domain/URL rating. That being said, there are scenarios where the benefit of forcing your score up those last few points starts being detrimental to other areas. This can sometimes be found with a technical site health score or with load speeds.




